GPA's aren't magical mathematical equations. GPA's are simply simplified representations that reflect your academic achievements. If you've been putting forth effort and seriousness in your studies, your GPA will show it. But it's important to remember that a GPA is not the end-all-be-all of success. It is only the result of hard work. Here are some ways you can boost your GPA.
Weighted grade point average
When calculating a student’s weighted Grade Point Average, it will be taken into account how many college courses they have taken. It is calculated using the marks for all courses, including repeated ones, and divided by the number credit hours. A=2.5 for advanced courses, A=1.5 for honors courses, and A=2.50, A=1.5 and D= respectively will be used by standard classes. The average will determine the student's rank in their class.
Another issue that weighs grades is their use as a disincentive to students. Students are encouraged to take more difficult courses by using the weighted system. It also removes any potential disincentive from getting a lower grade in a course that is harder. Furthermore, weighted grades are more balanced, recognizing higher levels of academic accomplishment. This information is crucial and should be investigated and reported by reporters and college counselors.
Unweighted grade point average
The most popular measure for college students is the unweighted grade-point average (GPA). There is a lot of advice available, but most of it doesn't apply unless you are taking extremely competitive classes. There are many options to increase your average, without sacrificing academic performance. These are the most popular methods. These strategies can help you improve your GPA.
The grades earned in each course determine the Unweighted grade average. This means that if the same course is taken more than once, the higher grade will be used. For each grade, there are different point values. A is worth 2.5 for advanced courses and B is worth half. And D is. Class rank is determined by the Unweighted Grade Point Average.
Calculating the grade point average
A grade-point average (GPA), or grade point score, is a measurement that measures an individual's academic achievement. It is the sum total of all grades earned in different courses throughout a semester. The grade of students can vary depending on their school and whereabouts they are from. This grade calculator will accept letter grades, and convert them to numbers. Grades range from 0.0 to 4. A high GPA is considered to be a desirable indicator of academic achievement.
If they aren't satisfied with their grade, students can withdraw from classes. While "W" grades are recorded on student records, they do not count in the calculation of grade point average. If a course is dropped because of non-participation, the student must replace it as soon as possible. During this time, the student's permanent records will display an "IP” symbol. The class will be completed with a substantive grade or unit of credit. A student cannot graduate with an IP grade.

Calculating a cumulative Grade Point Average
Students should learn how to calculate their cumulative grade points average (GPA). This measure shows you how well you are doing academically throughout college. It is important to know how many credit hours you have earned in order calculate your GPA. Add the semester GPA to the number credits taken. Divide the total number of semesters by it.
Most institutions will provide a list listing numeric equivalents of letter grades. This list will help you determine your GPA. You can then use the calculator to calculate you GPA once you have all of this information. The calculator will only give you an estimate. Make sure to read the rules of your institution. For more information on how to calculate your GPA using numeric equivalents, consult the institution documents.
FAQ
How do you get scholarships?
Scholarships are grants that can be used to pay college costs. There are many types to choose from. These are:
-
Federal Grants
-
State Grants
-
Student Loans
-
Programs for Work Study
-
Financial Aid
Federal grants come directly from the U.S. government. Most federal grants require applicants to meet certain requirements. For example, you must demonstrate financial need.
State grants can be offered by the individual states. These funds are offered by individual states based on financial need. Others offer money for specific purposes.
Banks and other lending agencies can provide student loans. Students borrow money to pay tuition and other living expenses.
Employers can use work-study programmes to attract qualified students. Employers must pay their employees at least the minimum wage.
Financial aid is available to help low-income families pay for college. It covers all or most of the tuition costs.
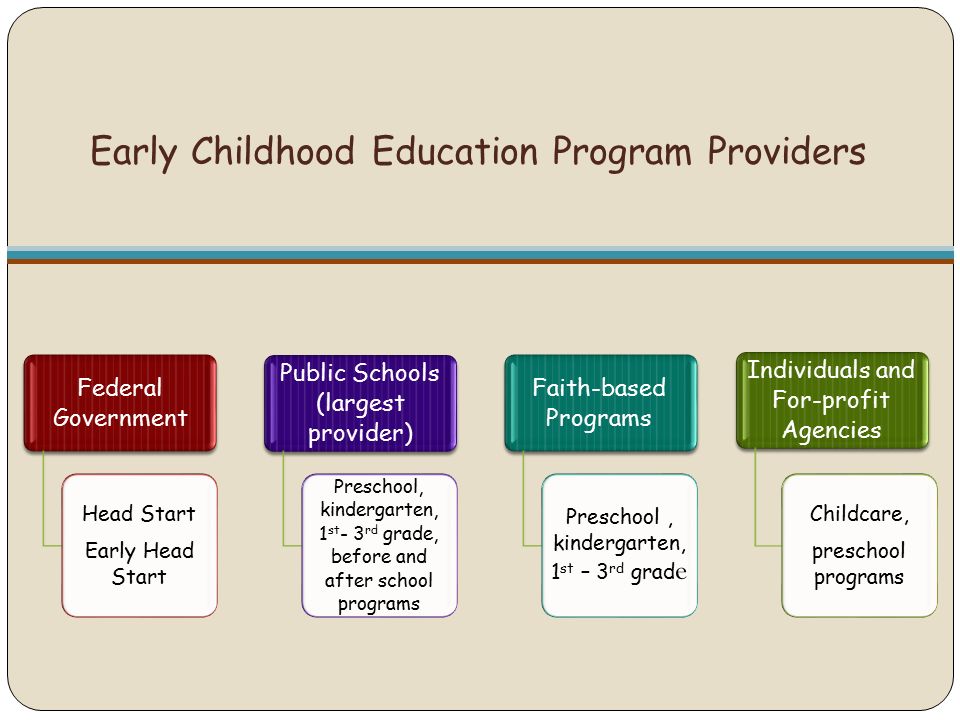
What are the requirements to be a teacher in early childhood education?
First, you must decide if early childhood education is what you want to pursue. You will need to earn your bachelor's degree if you decide to pursue a career in early childhood education. Some states require students to earn a master's degree.
You will likely also have to attend classes in the summer months. These courses can be taken to learn about topics such as pedagogy and curriculum design.
Many colleges offer associate degrees that lead directly to a teaching certificate.
While some schools offer certificates or bachelor's degrees in early childhood education, others only offer diplomas.
You may not require additional training if you are planning to teach at your own home.
What does it mean to be a teacher in early childhood education?
A teacher in early childhood education must have specific training. Before being permitted to teach in public schools, most states require that candidates for teaching positions have been certified by a state board.
Some states require teachers pass reading and math tests.
Some states require that teachers have completed a minimum number of courses related to early childhood education.
Many states have minimum requirements for teachers. These requirements can vary from one state to the next.
What are the differences between early childhood education?
There are many ways that early childhood education can be described. These are the most popular:
-
Preschool - Children ages 2 to 5
-
PreKindergarten: Children 4-6 years old
-
Head Start/ Headstart - Children ages 0 to 3
-
Day Care/ Daycares - Children ages 0 to 5
-
Child Care Centers – Children aged 0-18
-
Family Child Care – Children aged 0-12
-
Home Schooling - Children ages KG to 16
How much does homeschooling cost?
Homeschooling comes with no fees. Some families charge between $0-$20 per lesson. Other families offer free services.
But homeschooling is not easy. It requires commitment and dedication. Parents must have enough time to devote to their children.
Access to books, materials, and other learning aids is essential. To supplement their education, homeschoolers may need to use community programs and events.
Parents should consider the cost of transportation, tutors, extracurricular activities, and other expenses.
Homeschoolers also need to plan for field trips, vacations and special occasions.
What is the difference between public and private schools?
Public schools are free for all students. They provide education from kindergarten through high school. Private schools charge tuition fees for each student. They offer education from preschool until college.
There are also charter schools, which are publicly funded but privately run. Charter schools do not follow the traditional curriculum. They give students more freedom and allow them to pursue their interests.
Charter schools are popular with parents who believe their children should receive quality education regardless of their financial status.
Statistics
- And, within ten years of graduation, 44.1 percent of 1993 humanities graduates had written to public officials, compared to 30.1 percent of STEM majors. (bostonreview.net)
- Data from the Department of Education reveal that, among 2008 college graduates, 92.8 percent of humanities majors have voted at least once since finishing school. (bostonreview.net)
- They are more likely to graduate high school (25%) and finish college (116%). (habitatbroward.org)
- Think of the rhetorical power of nineteenth-century abolitionist Harriet Beecher Stowe, Martin Luther King, Jr., or Occupy Wall Street activists with their rallying cry of “we are the 99 percent.” (bostonreview.net)
- They are also 25% more likely to graduate from high school and have higher math and reading scores, with fewer behavioral problems,” according to research at the University of Tennessee. (habitatbroward.org)
External Links
How To
What is vocational training?
Vocational Education, which is an educational system that prepares high school students for jobs after college or high school, provides them with training in specific skills required for a job (e.g. welding). It includes training on the job in apprenticeship programs. Vocational education is different from general education in that it prepares individuals for specific career paths rather than acquiring broad knowledge for future uses. Vocational education does not prepare students for university, but it helps them find work after graduation.
Vocational education is available at all levels of education, including primary, secondary, high school, college, universities, technical institutes as well as trade schools, community colleges and junior colleges. Many specialized schools are available, including nursing and culinary schools, law schools medical and dental schools, veterinary medicine school, veterinary medicine schools, firefighting training schools, police academies, military academy, and other military schools. These schools offer both practical and academic training.
Over the past decade, a number of countries have made substantial investments in vocational education. These include Australia, Denmark and Finland, Germany. The effectiveness of vocational training is still a controversial topic. Some critics believe it doesn't help students get hired, while others claim that it helps prepare them for life after high school.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics has estimated that 47% of American adults hold a postsecondary certificate or degree related to their current occupation. This figure is higher among those with more education: 71% of workers aged 25-29 with a bachelor's degree or higher are currently employed in fields requiring postsecondary credentials.
In 2012, the BLS reported that nearly half of the nation's adult population had at least some form of postsecondary credential. One-third of Americans had a two year associate degree. Only 10% held a four-year bachelors degree. One out of five Americans held a master's degree or doctorate.
In 2013, the median annual wage for persons holding a bachelor's degree was $50,900, compared to $23,800 for those without a degree. The median wage for advanced degrees holders was $81,300.
For those who did no high school, the median salary was only $15,000. For those who did not complete high school, the median annual salary was only $15,200.